(In Proakis & Salehi unless otherwise noted)
Review: Ch. 5 Sec. 5.1
Do 5.11, 5.12
Hints on 5.11
Part 3) You can't use Eq. 5.1.11 (Why?)
Use techniques discussed in class on 4/22.
Part 4) The integral you encounter is not too
hard. What is (d/dy)(exp(–y2/2
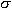 2))?
2))? Part 5) You can use Eq. 5.1.11.
Uniform, Gaussian, Q function,
Functions of random variables.
Read: Ch. 5 Sec. 5.1
Do: 5.3, 5.5, 5.9, 5.10
Read: Ch. 4 Sec. 4.2 to the end, Ch. 5 Sec. 5.1
Do 4.4, 4.5, 4.20, 5.1, 5.2
Note errata on Problem 4.20.
(no
kidding!)
Angle modulation, aka exponential mod.
Read Chapter 4 through Section 4.1 (thru p165.)
Do 3-A (not in textbook), 4.1, 4.2
Note textbook errata on page 163.
Read 3.2.3 through end of Chapter.
Do 3.11, 3.17, 3.24, The problem below.
Find the image frequency for radio station WNAX.
WNAX transmits DSB-SC on a 570 kHz carrier.
Assume the receiver's intermediate frequency is
455 kHz and that the local oscillator runs at a
higher frequency that the R.F. carrier.
and demodulation of the above
Read Ch 3 Introduction through 3.2.2
Do 2.44, 3.1, 3.3, 3.5, and note errata on
pages 151 and 152, also. . .
Use a computer to plot Eq. 3.2.6 (page 127).
Let mn(t) = cos(2πfmt) and let a = 0.75, Ac = 10,
fm = 440 Hz, and fc = 20 kHz. Turn that case
in for a grade, but use your computer code to
explore. What happens if a > 1? (try a = 1.2)
What happens as fc is lowered toward fm?
Be sure your plots have enough samples. You
should have at least 10 samples per cycle of
of cos(2πfct) and you should plot at least one
cycle of mn(t).
Use a computer for the plots for 3.3.
Review 2.2, Read 2.3
Do 2.41, 2.43 part b only
Note: In class on Wed. 2/17 problem 2.44 was removed
from this assignment. It will be assigned later
Read Ch. 2, Sec 2.3, Review Sec. 2.2
Do 2.39, 2.42, and also evaluate this integral:
![Integral from minus inf.
to inf. of {[2exp(-5t) +sin(10(pi)t)]delta(t)}dt](Integral_1.png)
Also evaluate the convolution
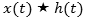
where
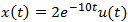
and
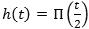
Read Ch. 2 Section 2.2
Do 2.37 and also find [Λ(t)sgn(t)u(t)] ★ u(t) where
sgn is the signum function and u is the unit step
function. The Lambda function represents the unit
triangle function and the star represents
convolution.
Optional: For a nice review and a few more
details, see how Prof. Oppenheim covers
Convolution in a 50 min. lecture at MIT.
Lecture 4, Convolution | MIT
Hint: You can watch it in 25 min. at 2x speed!
Note: On 2/03/2016 at about 5 PM Prof. De Boer added
brackets to the convolution problem's statment. The
brackets do not change the order of operations, but
they do make it easier to understand.
Review Ch 2 Sec. 2.1; Read Ch 2 Sec. 2.5.
Do 2.7, 2.24, 2.34
Note: On 2/01 Prof. De Boer corrected an error in the
reading assignemnt. He had posted "Sec. 2.2" which
was wrong so he changed it to "Sec. 2.5" which is
the actual material covered by problem 2.7.
Read: Ch 1 Sec. 1.4, Ch.2 through Sec. 2.1
Do (p. 101) 2.1 (all parts), 2.5, 2.6, 2.16.
Use a computer to make the plots for 2.1.
Octave or Matlab are recommended.
Here is a m-file to get you started.
DDB's "Toolbox" files including u.m, rect.m,
sinc.m and triangle.m can be downloaded as a
zip archive DDB_TBX.ZIP.
Hint: At the command line in Octave or Matlab
type, "help sign" [enter]. Also try
"help addpath", "help help" and "help exit".
After file rect.m is on the path-list, note
happens when you type "help rect" in the
command window. Compare to the comments in
the source file, rect.m.
Note errata on pages 29 and 42, and 101, 102.
Read Chapter 1.
(There is nothing to turn in.)