#
(In Alexander & Sadiku unless otherwise noted.)
----
----
Review for final exam
Optional: Clips from the PBS show, "Rickover:
the birth of Nuclear Power." (Full program
will air on Iowa Public TV's "World" channel,
Premier Cable channel 28, Thursday, 12/11 at
3 AM, with a re-run on Friday, 12/12 at 6 PM,
Premier cable ch 28 and over-the-air ch 27.3)
12/10
at
5 PM
12/11
Read: 13.1, 13.2, 13.5
Do: 13.36, 13.37, 13.52
On Wednesday, 12/10 there will be a box labeled
"EGR 220 Homework" near Prof. De Boer's office
door. Drop your homework in the box by 5 PM
Wednesday, 12/10 for final grading.
This problem set will be graded and ready for
pickup by 5 PM Thursday, 12/11. Pick your
homework up from the box near Prof. De Boer's
office door on Thursday evening or Friday.
12/10
12/11
Read 12.10, 12.11
Do 12.71, P11.6-6 from
another textbook. (Your web brouwser must be
logged into Canvas@Dordt for the above link
to work.)
Hint on P11.6-6: The power angle is defined
as (θv – θi) but θv = 0 due to the location
of the given reference node. Then what is θi ?
Note errata on pages 534-535 and 537 and 541
and the answer to 12.71 and the
alternative development of Eq. 12.67.
Optional Reading: more on "Split-Phase" and on
"High-Leg Delta" (also called red-leg, orange-
leg, wild-leg, stinger-leg, bastard-leg and similar
". . . leg" names) and still more on "Open-Delta"
(scroll to last section of the page)"
This problem set will be graded and ready for
pickup by 5 PM Thursday, 12/11. Pick your
homework up on Thursday evening or Friday from
a box that will be located near professor
De Boer's office door.
Optional: "How to wire a split-phase elec. panel"
12/08
12/10
S = P + jQ = √3VLIL/θ
Read 12.7
Do 12.33, 12.36
Note errata on Problem 12.36 part (c).
Optional: CDMA cell phone modulation
done with direct-sequece spread-spectrum
12/05
12/08
Various connections between Y and Δ
Read 2.7, 12.4, 12.5, 12.6
Do 2.51, 12.11, 12.14
Note errata on pages 512 through 519.
Note errata on Problems 12.11 and 12.14
Optional:
DVD at the DC Library: "Flash of Genius"
You Tube trailer; Rotten Tomatos review
✽"Too much technical information about circuit boards,
Motorola transistors. . ." —Rex Reed
☻"Ethics is at the heart of this David and Goliath "
story. . . —Louise Keller
12/03
12/05
Read 12.1, 12.2, 12.3
Do 12.5, 12.7, 12.10
Note errata on pages
506 through 512 (5 corrections alltogether).
Note errata on the answer to Problem 12.5.
Note errata on Problem 12.7.
Note errata on Problem 12.10.
Note 1.) All voltages and currents given
in Chapter 12 are RMS unless otherwise noted.
Note 2.) "Determine the current," means "find
the RMS value of the current," which is what
an AC ammeter does. There is no angle in the
answer. Only give phasors as answers when
phasors are requested.
Note 3.) Use the phasor transform when
possible. It makes these problems easier.
Optional:
Video on Frequency-Hopped Spread Spectrum
Read about Lamarr, inventor of FHSS
Book Review: "Hedy's Folly"
11/24
12/03
Read 11.9, 11.10
Do 11.77, 11.80, 11.84
Note errata on Problems 11.51 and following.
Note errata on Problems 11.80 and 11.84.
Note: Lab report is due 12/05 at 10:00 am
Optional video on a Heisenberg compensator.
11/21
11/24
Power Factor Correction
Read 11.7, 11.8
Do 11.63, 11.69, 11.91
Note errata on Problems 11.51 and following.
Note errata on the answer to Problem 11.69(b).
Note errata on the answer to Problem 11.91.
Optional reading: Another perspective on
power factor correction. (DDB prefers this method.)
11/19
11/21
Complex Power, the Power Triangle
Read 11.5, 11.6
Do 11.41, 11.47, 11.48,
Note errata on definition of power factor.
Note errata in Equation 11.51, page 475.
Note errata on Problem 11.48.
Optional video on encabulator technology.
Optional reading on encabulator technology.
11/17
11/17
Read 11.4
Do 11.24, 11.25, 11.29
Note the footnote on the bottom of page 490.
Also, please return PS#27 on 11/14 so that
grades can be recorded.
Optional: Yet another video here
11/14
11/17
reactive power, and power factor angle
maximum power transfer theorem redux
Read 11.1, 11.2, 11.3, Extension of Eq. (11.5)
Do 11.1, 11.3, 11.13
Note errata on page 464.
Note errata on Problem 11.13.
Optional: What do you think of this video "You see it's aah... drawin' about two amps of power... now I'm gona plug this in... and it's gone down to about one and a half amps of power..." (Quotation from the video.)? And,
if you liked that one, you might also like this one! "...converts one power source and puts it into four, each costing 25% of the electricty..." (Quotation from the video.)
We can discuss these cliams in class if you like.
11/12
11/14
Read 10.4, 10.5, 10.6, 10.10
Do 10.7, 10.54, 10.55
Note errata on the answer to Problem 10.55
Note: Prof. De Boer forgot to post the assignment
number and due dates on Friday when he routinely
should have. He posted these on Saturday evening.
If this caused a problem for you, please speak with
him or e-mail him about it.
11/10
11/12
Topics: KVL with phasors (like vector addition),
and Sinusoidal Steady-State Circuit Analysis
Read 9.7, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3
Do 9.59, 9.90, 10.27
Hints for 9.90: KVL around the loop using the
three labled phasors is helpful. The phasors
form a triangle. Take V1 as the reference phasor
(has angle zero). A graph of these phasors
drawn to scale can be helpful to estimate
angles for the phasors and the "Law of Cosines"
can be used to find them analytically. Once
the three phasor angles are known the loop
current phasor can be found, etc.
11/07
11/10
Review 9.3, Read 9.4, 9.5
Do 9.23, 9.25, 9.29, 9.35
Note errata on problems 9.23 and 9.29 and 9.35
Also look over the test coverage on the
"Canvas course page" before Monday.
Optional: Java applets on phasors 1, 2, 3.
Optional (recommended for the above phasors
applets): Bypass Java security settings.
11/03
11/07
Read 9.3
Do 9.9, 9.11, 9.12, 9.19
Note errata on the answers to
Problems 9.9(a) and 9.11(d).
Optional Reading:
Prof. De Boer's notes on sinusoidal steady state
10/31
11/03
Read 9.1, 9.2, App. B on pages A-9 through A-15
Do 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.13
Note trigonometric identities in Appendix C.
Note errata on the answer to Problem 9.1
Optional Reading:
Prof. De Boer's notes on complex numbers
Optional videos:
A.) A non-conventional intro. to complex #s
B.) A conventional lecture on phasors ~38 mins.
Note two typos in the above lecture on phaosrs.
1.) at 5:45 "cos(ωt +
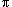 /2)"should be "cos(ωt +
/2)"should be "cos(ωt + 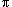 /4)"
/4)"2.) at 21:58 in two instances, the word "conductive" in
blue text should be replaced by "capacitive" in blue text.
10/29
10/31
Read 8.7, 8.11, 8.12
Do 8.45 except change the 2 Ω resistor
to 1 Ω. The answers then are v(t) = 6e-tsin(t) V
and i(t) = 4 – 3e-t[cos(t) + sin(t)] A
Also do 8.61
Note errata on Problem 8.45
Optional: Read 8.10. Note errata on page 350
Optionsl: Wikipedia on "Pinch (plasma physics)"
10/27
10/29
Review 8.4, Read 8.5, 8.6
Do 8.24, 8.37
Optional: RLC Resonant Circuit
Another classic demo of RLC
10/24
10/27
over- critically- and under-damped.
Review 8.3, Read page 323 to end of
Section 8.3, and all of Section 8.4.
Do 8.9, 8.14, 8.23
Note errata on the answer to Problem 8.9
Note errata on Problems 8.14 and 8.23.
Note errata on pages 321 and 323 and I-3.
Optional: Damped Mass on a spring
10/22
10/27
RLC over-, under-, and critically-damped
Read 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 only through page 322.
Do 8.1, 8.4, 8.7
Note errata on pages 321 and 323 and I-3.
Optional: Resonance Experiment
Wine glass resonance in slow motion
10/20
10/22
Review Ch. 7 Sec. 1-6, Read 7.9, 7.10
Do 7.28, 7.31, 7.85
Note errata on the answer to Problem 7.31
Optional: How a crystal radio works
10/17
10/20
Read 7.5, 7.6
Do 7.39, 7.47, 7.51
Optional: "Over-Under" cable wrapping
here and here.
10/15
10/17
Review 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, Read 7.4
Do 7.4, 7.13, 7.27
Optional: Electric Guitar Modification
Optional: Biwin: we make better tomorrow
10/13
10/15
Read 7.1, 7.2, 7.3
Do 7.1, 7.2, 7.11
Optional: Huffman Coding
Optional: Fun with a high-voltage capacitor
Optional: Attend the Job Fair, 5:30 - 8:00 PM
10/10
10/13
Review 6.1 through 6.5, Read 6.6, 6.7
Do 6.6, 6.21, 6.67
Note errata on Problem 6.67 and
the answer to Problem 6.67.
Optional: Analog Music Synthesizers
Optional: Emerson Breaks Down the Moog
Optional: McKechnie plays the Moog
Optional: 1 hour documentary "Moog" Disclaimer:
Prof. DB does not endorse everything in this
video!
10/08
10/10
Topics: Inductors, energy storage in mag-field,
series and || combinations of inductors
Read 6.4, 6.5
Do 3.15, 3.81, 6.40, 6.46
Note: Do 3.15 and 3.81 during lab. You must
solve them using the PSpice circuit simulator.
Optional: Railgun demonstration
Optional: How a railgun works.
10/06
10/08
series and || combinations of capacitors
Read 6.1, 6.2, 6.3
Do 6.5, 6.13, Repeat 6.13 except change the
60 V source to 40 V and change the 20 Ω
resistor to 50 Ω.
Note errata in Eq 6.5 and Eq 6.6 and this.
Note: Please review homework standards for
matters on the size and quality of graphs that
are answers.
Optional video: What is inside a capacitor?
9/29
10/06
Read 5.7, 5.8, 5.10
Do 5.50 part (a) only, 5.66, 5.88
Hint for 5.66: Nodal analysis looks messy since
there are so many nodes, but actually it turns
out to be easy due to the voltage sources and
the grounded non-inverting inputs to the op-
amps. There are only two nodes at which full
KCL equations are needed.
Hint for 5.88: There are two voltage dividers
in the diamond-shaped group of resistors (the
"bridge") and one instrumentation amplifier in
the given circuit.
Optional: Find out more about power steering.
9/26
9/29
(rtn'd
after
class,
see
your
e-mail)
Read 5.4, 5.5, 5.6
Do 5.19, 5.27, 5.39.
Optional: Learn more about decibels via the
wikipedia or The University of New South Wales
or take a free hearing test to hear what
"decibels" mean to you.
Optional: Diesel engine governers explained
9/24
9/26
Read 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 14.3 (page 617-618)
In Section 14.3 note equation 14.10.
Do 5.1, 5.5, 5.9
Hint for 5.1: In the application of Eq. 14.10 to
Problem 5.1 assume R1 = R2. The phrase
"voltage gain" is a signal to use this
assumption even if it is untrue.
Hint for 5.9: Since the specifications for the
op-amp (Ri, Ro, A) are not given, assume it is
ideal. This is the customary practice whenever
the data needed to describe non-ideal behavior
is not given.
Note errata on the answer to Problem 5.5
Optional: View this anamated tutorial From ASU
on the topic of the ideal op-amp.
The tutorial uses the word impedance. This is a
generalization of resistance. We will study impedance
later in this course. For now, just consider it to mean
the same thing as resistance. (Z = R)
9/22
9/24
Read 4.8, 4.10
Do 4.67, 4.68
Optional: Fractal Zoom... Mandedelbrot (10:01)
9/19
9/22
Review Examples 4.8, 4.9, 4.10 (pgs 140-145)
Read 4.6. Optional: Read 4.7
Do 4.39, 4.47, 4.64
Note errata on the answer to Problem 4.47
Optional: Biography on Léon Charles Thévenin.
Optional: Thevenin's theroem in pop culture.
Optional: If you plan to go the the ISU
career fair, consider this advice from VT.
Dress code at this fair is interview attire!
Promo video of the career fair from ISU
It does not cost a fortune to look like $1M.
Good videos on dress from MNSU here.
9/17
9/19
Read 4.4, 4.5
Do 4.20, 4.23, 4.33
Note errata on problems 4.20 and 4.23
Optional:
Remembering Ray Dolby, 1/8/1933–9/12/2013
"Above all else, guard your heart, for everything you do
flows from it." — Proverbs 4:23 (NIV)
"I think a lot of developments start with the desire of
the developer to get what he really wants so that he can
use it. It's not just the technical fascination or the
business opportunity." —Ray Dolby
Ray Dolby, pioneering sound engineer, dies at 80
—San Francisco Chronicle
Retrospective Web site (includes a video)
—hosted by Dolby Labs
9/15
9/15
Read 4.1, 4.2, 4.3
Do 4.3, 4.6, 4.9
Note on Problem 4.3: For full credit on you
must use linearity for parts (b) and (c).
Note on Problem 4.6: For full credit you must
explain (use a sentence or two) how you got
your answers.
Optional video: The greatest Engineering
Achievements of the 20th Century. (~9 min.)
9/12
9/15
Read 3.7, 3.9
Do 3.62, 3.63, 3.89
Note: We will cover Section 3.8 in the lab.
Note errata on Page 109, Figure 3.40(b)
Hint on 3.89: Combine the 0.7 V source with
the 3.0 V source. Then use the transistor
model shown in Figure 3.40 (b), page 109.
Optional video from Bell Telephone in 1965
The Genisis of the Transistor (~17 min.)
9/10
9/15
Mesh, Supermesh
Read 3.4, 3.5.
Do 3.34, 3.41, 3.44
Note errata on Problem 3.34.
Note: we will skip Section 3.6 in the textbook.
It is optional reading however. Some students
find the method in Sec. 3.6 to be tricky (bad).
Others love it. "Your mileage may vary."
Optional: Why become an engineer? Watch this
short film titled Design Our Future.
Prof. De Boer does not endorse every statement made
in this video, but it does provoke thought.
(The link at the end of the video is defunct. A similar
link ending in ".info" instead of ".us" is a phishing
site—don't go there!)
9/08
9/10
Review 3.1, 3.2, Read 3.3
Do 3.4, 3.17, 3.18
Optional video ~3 minutes: "Every question
harbors a latent question." (What if?)
9/05
9/08
Read 3.1, 3.2 in your textbook
Optionally review Sections 7, 8, 13 in IEE.
Do 3.2, 3.7, 3.10
Optional:
Video lecture: The Passive Sign Convention
Video lecture: Passive Sign Cnvntn Examples
Note: The passive sign convention is easy once you
clearly understand it. However, there are lots of bad
descriptions of it floating around on the Internet.
Stick with the IEE handout, the videos above, or ask in
class rather than searching the Internet yourself on
this matter.
Oprional: Interveiw tips from GE
See
note
1
below
9/03
9/05
Read: 2.8, 2.9 in your textbook
Review: Sections 9, 10, 11 in the IEE handout.4
Do 2.67, 2.69, 2.74, from your textbook
Note errata on Page 59, Figure 2.55 part (b)
Note errata on Page 60, Practice Problem 2.16
9/01
See
note
2
below
9/03
See
notes
3 & 4
below
voltage, resistance, power, KVL, KCL
Scan Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 through
Section 2.6 in your textbook
Review sections 1 though 8 in the handout,
"An Introduction to Electrical Engineering."4
Do these end-of-chapter problems in your
textbook: 1.2, 1.11, 1.18, 2.10, 2.31.
Note errata in your textbook4 on
Practice Problems 1.2 (page 8) and Practice
Problem 2.8 (page 42). Also note additional
errata on pages 5, 9, 23, and 27. Also
note the systematic error with significant
figures in answers given in the appendix.