![]()
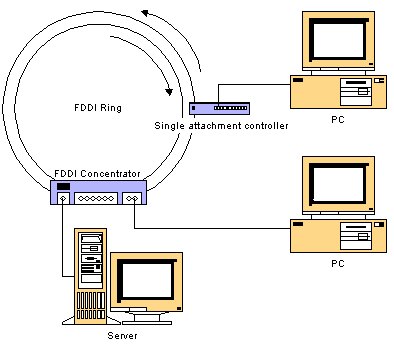
FDDI is a LAN technology offering 100Mbps data transmission rates over two counter-rotating fibre optic rings. Whereas ethernet uses CSMA/CD as its medium access control methodology, FDDI uses modified token passing. FDDI's MAC methodology is slightly different to that of token ring. Token passing guarantees that a transmitting network device has full bandwidth by ensuring that transmission can only take place once it possesses a 24 bit packet known as a token.
Each computer or group of computers can be assigned different amounts of bandwidth, known as synchronous bandwidth allocation (SBA). Frames are transmitted in a continuous (synchronous) stream and are prioritised according to the predefined SBA. Any spare network capacity can be filled by devices transmitting as and when they can (asynchronously).
FDDI is not standardised by the IEEE, instead it was ratified by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) X3T9.5 committee in 1984. It is known for its reliability which comes, in part, from the use of fibre optic media. Fibre optic is not subject to interference from electromagnetic or radio sources. One fibre ring is known as the primary, the other is a secondary ring that is used if the primary fails. Both rings are attached across a single controller. FDDI can support 500 connections with the total circumference of the ring nearing 200 kilometres (if repeaters are used every 2 kilometres). CDDI (copper distributed data interface) has been developed to support the functionality of FDDI over copper media. Copper wiring cannot support the 2 kilometre segments of fibre, but it can offer the same speeds (100Mbps) over 100 metre segments.
Computers can access the rings either by a single access controller or a dual access controller. As the names suggest, a single access controller attaches to one ring, whilst dual access controllers attach to both rings. Single access is cheaper, but the attached computer loses the redundancy benefits afforded by dual attachment. FDDI is interconnectable with ethernet across FDDI bridges.
| Interoperability Lab FDDI consortium | Good FDDI overview from the University of New Hampshire |
| Interoperability Lab FDDI tutorial | Well written tutorial |
| US Navy ANSI X3T12 homepage | Access to a FDDI FAQ |
| XLNT FDDI page | Good FDDI discussion |